Combinatorial Drugs for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders
Drug candidates to inhibit the progression of neurodegenerative disorders
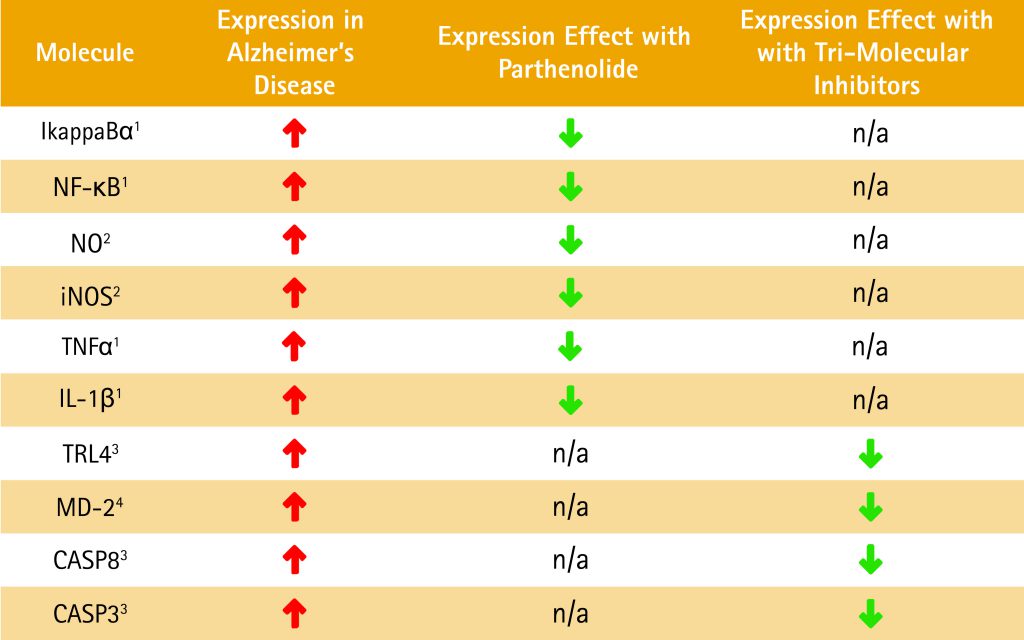
KAUST researchers have identified Parthenolide in combination with other well-known and characterized compounds as potential inhibitors of known pathways involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Advanced bioinformatics analysis reveals significant potential for Parthenolide to decrease the expression of six molecules (IkappaBα, NF-κB, NO, iNOS, TNFα, and IL-1β) associated with Alzheimer’s. The findings indicate that the major inflammatory pathways leading to the disease progression could be blocked when Parthenolide is used in combination with inhibitors of the tri-molecular receptor complex (TLR4/MD-2/CD14), such as Curcumin or Resatorvid, to reduce the processing and activation of caspase -8 and -3. The use of nACHR agonists such as Tilorone was also indicated to help restore normal cellular processes.
These combinations represent an opportunity to change the progression of Alzheimer’s disease whereas current drugs merely treat the disease’s symptoms. In addition, the compounds identified by the bioinformatics analysis at KAUST hold potential for treatment of other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Huntington’s.
Benefits
- Attacks the Source: Potential to inhibit the major known inflammation pathways that cause neurodegenerative disease
- Therapeutic, not Palliative: Changes the progression of neurodegenerative diseases instead of only treating the symptoms
- Established Compounds: The proposed combinations employ compounds that are well-known and extensively characterized by the scientific community

Applications
- Development of OC diagnostic kits
- Central laboratory testing
- Point-of-care diagnostics
- Complementary diagnostics for pharmaceuticals
- Personalized medicine
- Pharmaceutical screening research
- Test development for clinical genomics and diagnostics companies