Repositioned Drug Candidate for the Potential Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
Synergistic conbinations of Hydroxyfasudil and fetal hemoglobin (HbF) inducers
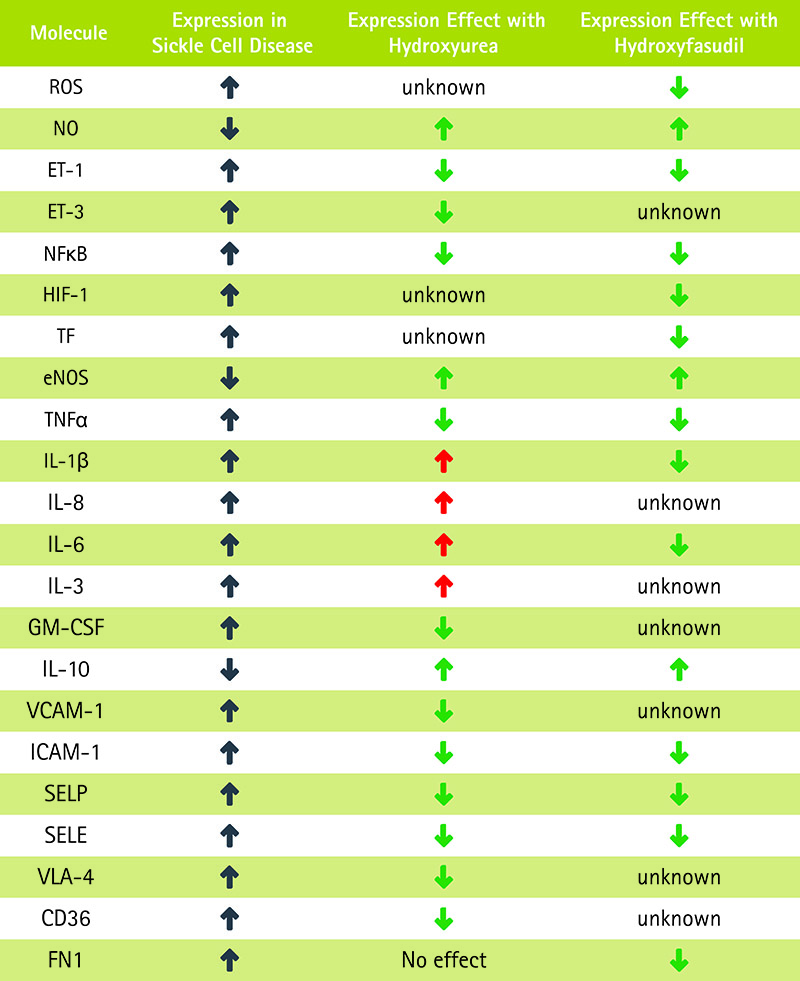
KAUST researchers have identified a combination therapy including the Rho-kinase inhibitor Hydroxyfasudil and HbF inducers as a potential sickle cell disease (SCD) treatment. Advanced bioinformatics analysis strongly indicates that Hydroxyfasudil has the potential to treat SCD symptoms in a manner similar to the current treatment of choice, Hydroxyurea, but with fewer side effects. Hydroxyfasudil is currently approved to treat cerebral vasospasm and pulmonary hypertension in China and Japan.
Key factors in SCD treatment are: 1) Relieving the vaso-occlusive crisis, 2) reducing inflammation, and 3) stimulating HbF production. Hydroxyfasudil offers a potentially superior solution to Hydroxyurea for the reduction of inflammation and alleviating the painful vaso-occlusive crisis. The incorporation of HbF inducers (e.g. sodium butyrate, decitabine) addresses the third critical component of effective SCD treatment.
Taken together, this drug synergy approach coupling Hydroxyfasudil with the most effective HbF inducer(s) could replace or enhance Hydroxyurea therapy, whilst eliminating or reducing the associated side effects.

Benefits
- Effective: Provides potentially superior relief of the three key symptoms of SCD compared to current treatment options
- Reduced Side Effects: Reduces inflammation where current Hydroxyurea treatments actually exacerbate chronic inflammatory SCD states
- Efficient: Repurposing of a compound already approved for the treatment of medical conditions
Applications
- Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease